TACKLING ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE: STILL SOME GAPS
Countries are making significant steps in tackling antimicrobial resistance (AMR), but serious gaps remain and require urgent action.
This is according to a report released by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Wide discrepancies
The report charts progress in 154 countries and reveals wide discrepancies. Some, including many European countries, have been working on AMR policies in human and animal sectors for more than 4 decades. Others have only recently started to take action to contain this growing threat. Progress in developing and implementing plans is greater in high-income than low-income countries but all countries have scope for improvement. No country reports sustained capacity at scale in all areas.
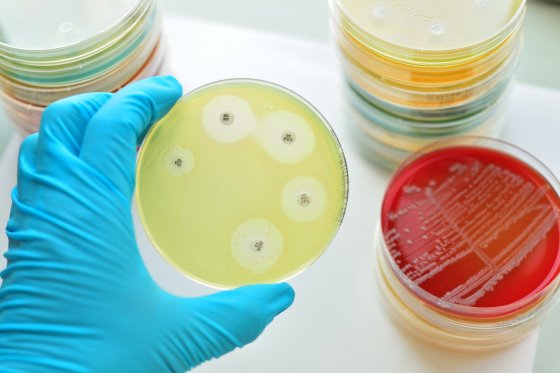
Photo: Jarun Ontakrai / Shutterstock
Regulating policies
Promising findings include 105 countries with a surveillance system in place for reporting drug-resistant infections in human health and 68 countries with a system for tracking consumption of antimicrobials. In addition, 123 countries reported that they have policies to regulate the sale of antimicrobials, including the requirement of a prescription for human use – a key measure to tackle overuse and misuse of antimicrobials. But implementation of these policies varies and unregulated medicines are still available in places such as street markets, with no limits on how they are used. Medicines are very often sold over the counter and no prescription is requested. This puts human and animal health at risk, potentially contributing to the development of antimicrobial resistance.
A total of 67 countries report at least having legislation in place to control all aspects of production, licensing and distribution of antimicrobials for use in animals. But 56 either said that they had no national policy or legislation regarding the quality, safety and efficacy of antimicrobial products used in animal and plant health, and their distribution, sale or use, or that they were unable to report whether they have these policies in place. There is also a substantial lack of action and data in the environment and plant sectors. Although 78 countries have regulations in place to prevent environmental contamination generally, only 10 of them report having comprehensive systems to ensure regulatory compliance for all waste management, including regulations that limit the discharge of antimicrobial residues into the environment. This is insufficient to protect the environment from the hazards of antimicrobial production.
Dedicated OIE international standards
“Supporting low- and middle-income countries to follow guidance of responsible and prudent use of antimicrobials in animals is an urgent priority,” says Dr Matthew Stone, deputy director general of the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). He adds: “Implementation of dedicated OIE international standards, appropriate national legislation and strengthening of veterinary services are essential steps to help all animal health stakeholders contribute to controlling the threat posed by antimicrobial resistance.” Maria Helena Semedo, FAO Deputy director general commented: “FAO welcomes that many countries are taking concrete steps towards the responsible use of antimicrobials in agriculture. However, countries need to do more to reduce the unregulated and excessive use of antimicrobials in agriculture. We particularly urge countries to phase out the use of antimicrobials for growth promotion in animal production – terrestrial and aquatic.”
Source: FAO
Emmy Koeleman
Editor: All About Feed & Dairy Global
Source: www.allaboutfeed.net